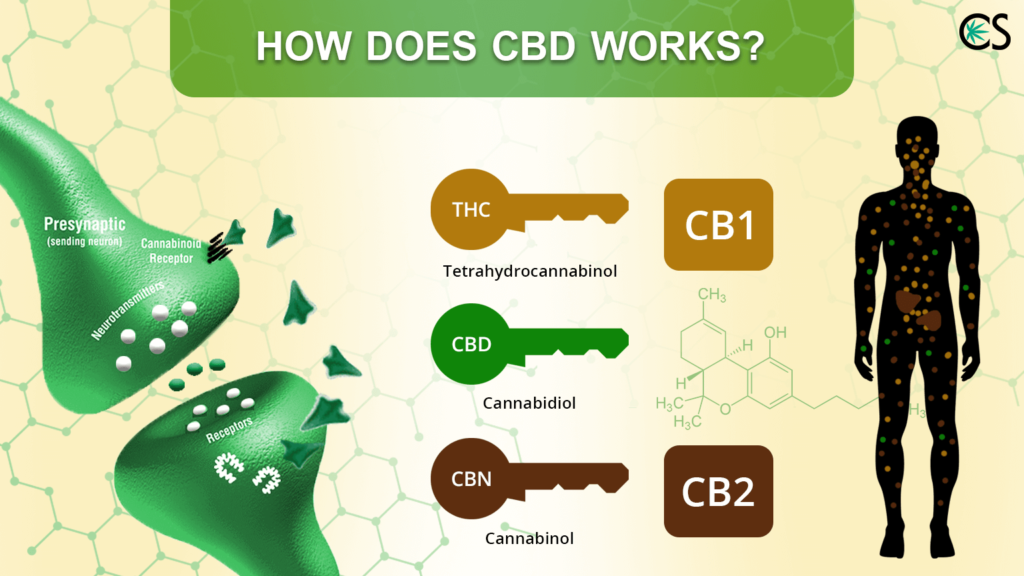
Cannabidiol (CBD) stands out among the array of active compounds found in cannabis. Unlike tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), CBD is non-psychoactive, meaning it doesn’t induce a “high.”
What precisely are the effects of CBD?
While the exact mechanism of CBD’s action remains somewhat elusive, there is speculation that it may modulate cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2. These receptors play a role in regulating functions like sleep, mood, and appetite within the endocannabinoid system (ECS).